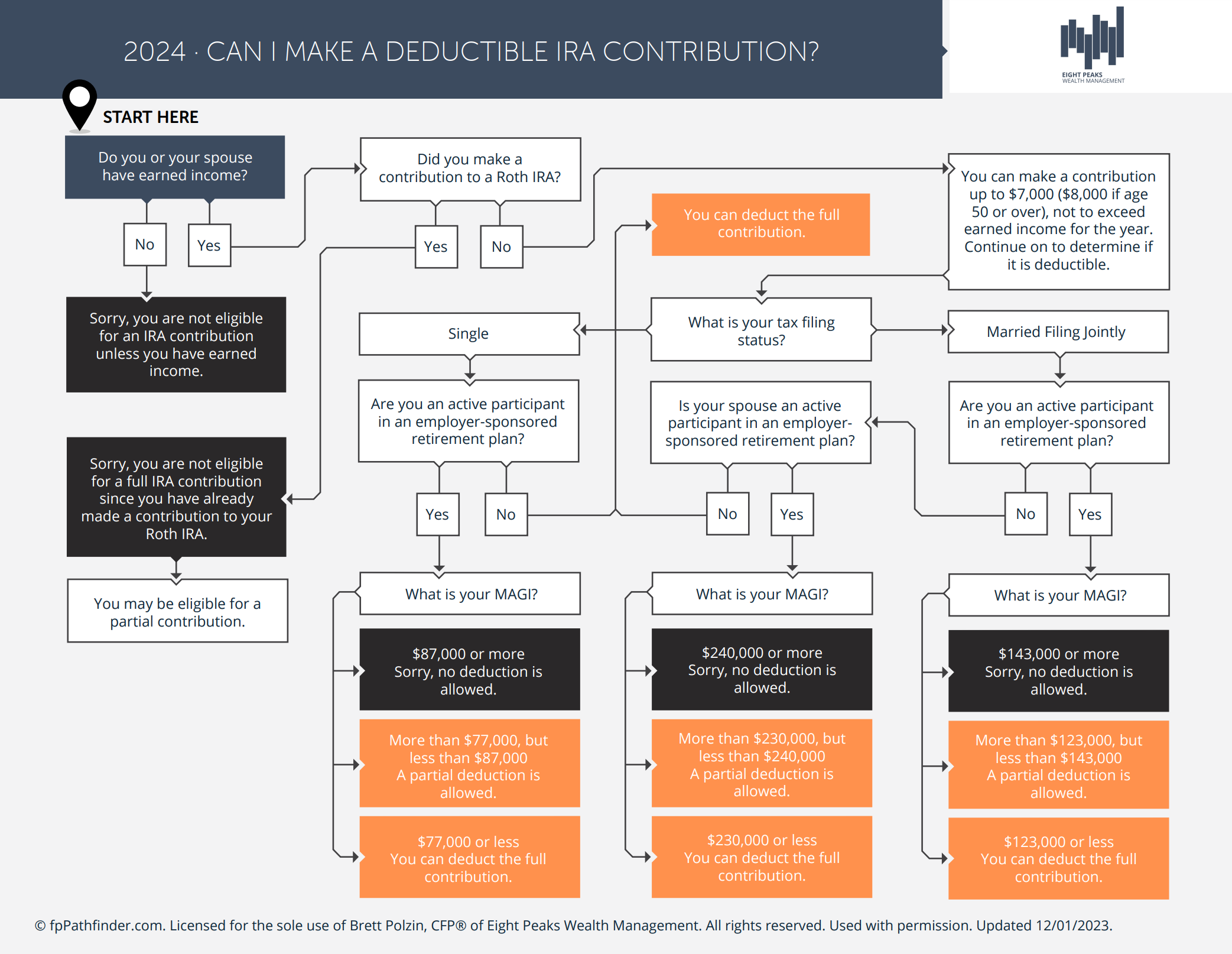
Understanding the Deductibility of Traditional IRA Contributions
Saving for retirement is a crucial aspect of financial planning, and a Traditional IRA (Individual Retirement Account) offers a tax-advantaged route for many. However, navigating the eligibility for contributions and understanding the tax deductibility of those contributions can often seem daunting. To assist in this process, we've developed a tool: the "Can I Make A Deductible IRA Contribution?" flowchart. This visual guide simplifies the complexity surrounding Traditional IRA contributions, focusing on several key factors:
1. Earned Income
To contribute to a Traditional IRA, you must have earned income. This fundamental requirement ensures that individuals are actively receiving compensation, such as wages, salaries, or self-employment income, which qualifies for IRA contributions.
2. Coverage Under an Employer Plan
Whether you or your spouse are covered by a retirement plan at work significantly influences your ability to deduct Traditional IRA contributions. Being covered by an employer's retirement plan can introduce limitations on the deductibility of your contributions based on your income level.
3. Other (Roth) IRA Contributions
Your contributions to a Roth IRA can also affect your eligibility for making deductible contributions to a Traditional IRA. Since Roth IRAs are funded with after-tax dollars and offer tax-free growth and withdrawals, the rules governing contributions to both account types ensure a balanced approach to retirement savings.
4. Filing Status-Based MAGI Thresholds
Your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) plays a pivotal role in determining the deductibility of Traditional IRA contributions. The IRS sets specific MAGI thresholds based on your tax filing status (e.g., single, married filing jointly) that dictate the extent to which your contributions can be deducted.
The "Can I Make A Deductible IRA Contribution?" flowchart is designed to address these common factors that impact eligibility rules for traditional IRAs. By considering each of these aspects, you can gain a clearer understanding of how to maximize the benefits of your IRA contributions.
This tool is particularly valuable for financial advisors and clients alike, as it provides a straightforward method for assessing eligibility for deductible IRA contributions. With this knowledge, you can make more informed decisions that align with your long-term retirement goals.
Remember, while this guide offers a starting point, individual financial situations can vary widely. It's always recommended to consult with a financial advisor to understand how these rules apply to your specific circumstances and to navigate the complexities of retirement planning effectively.